3 min read
NASA’s IMAP Mission Captures ‘First Light,’ Looks Back at EarthMara Johnson-Groh
Dec 16, 2025 ArticleAll 10 instruments aboard NASA’s newly launched IMAP (Interstellar Mapping and Acceleration Probe) mission have successfully recorded their first measurements in space. With these “first light” observations, the spacecraft is now collecting preliminary science data as it journeys to its observational post at Lagrange point 1 (L1), about 1 million miles from Earth toward the Sun.
“We are extremely pleased with the initial in-flight performance of the IMAP mission. All instruments have successfully powered on and our commissioning remains on track. We have already collected useful data including exercising our near-real-time space weather data stream,” said Brad Williams, IMAP program executive at NASA Headquarters in Washington. “This successful milestone is quickly setting the stage for the start of our primary science operations."
As a modern-day celestial cartographer, IMAP will chart the boundaries of the heliosphere — a huge bubble created by the Sun's wind that encapsulates our entire solar system — and study how the heliosphere interacts with the local galactic neighborhood beyond.
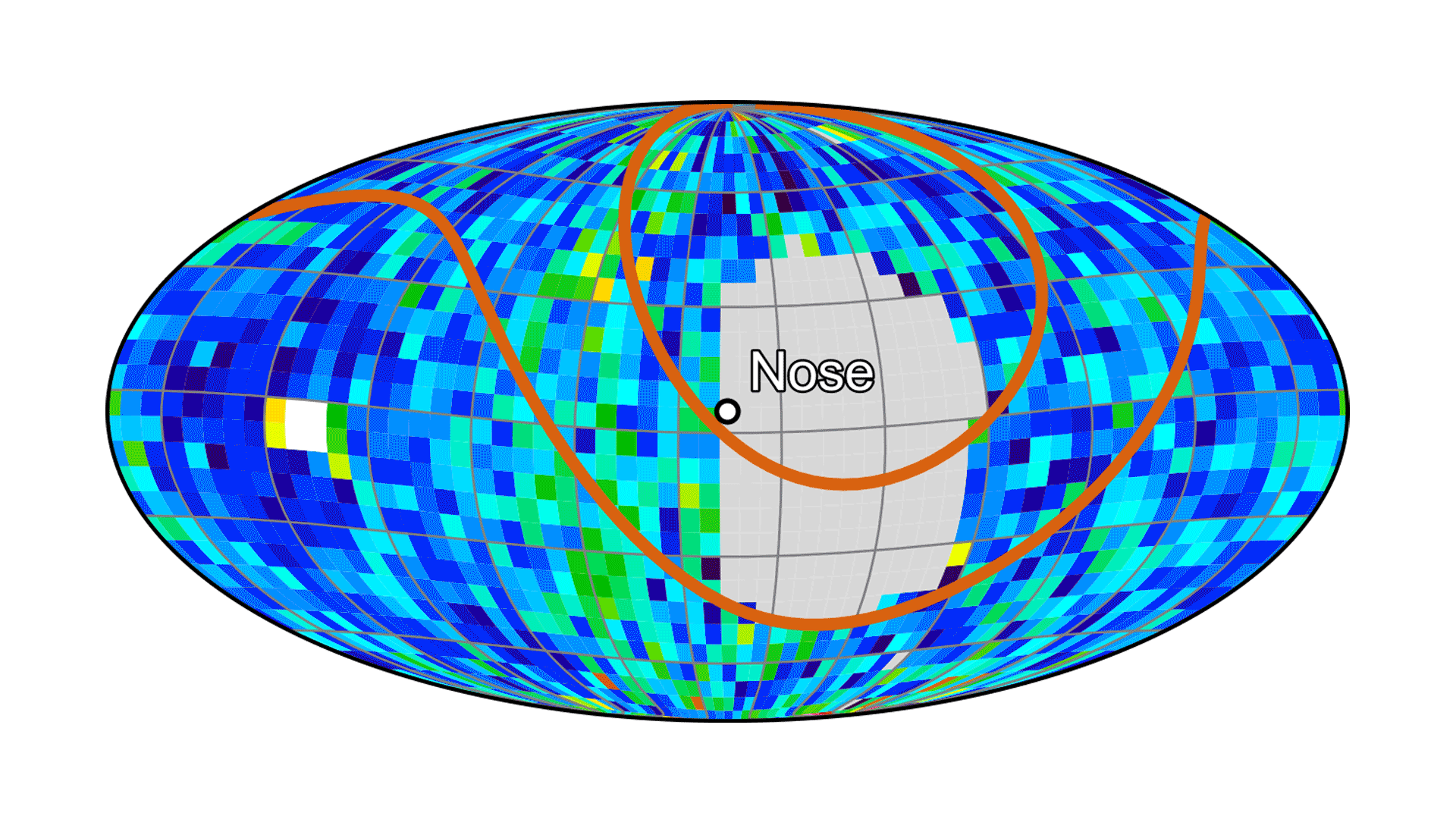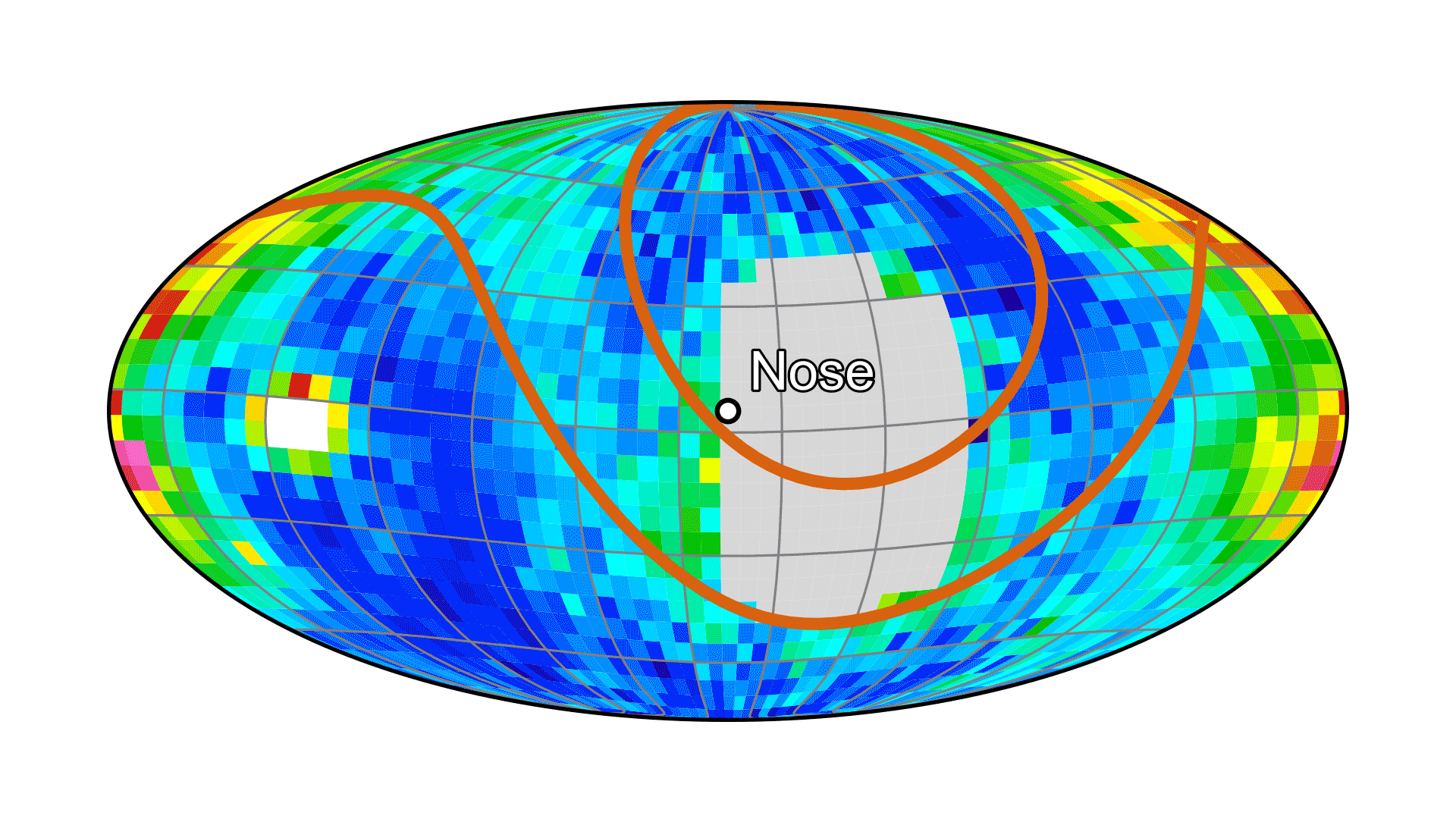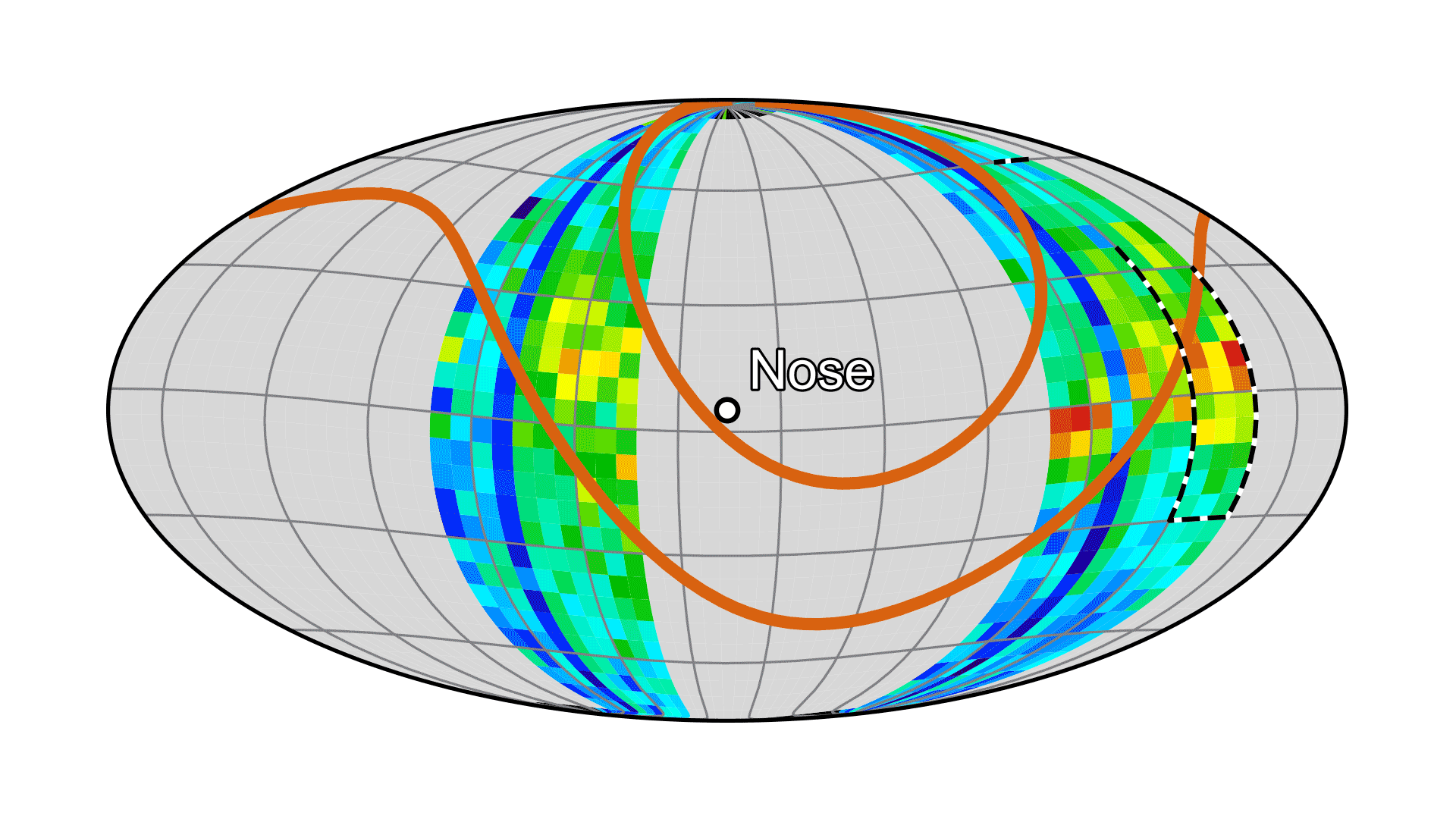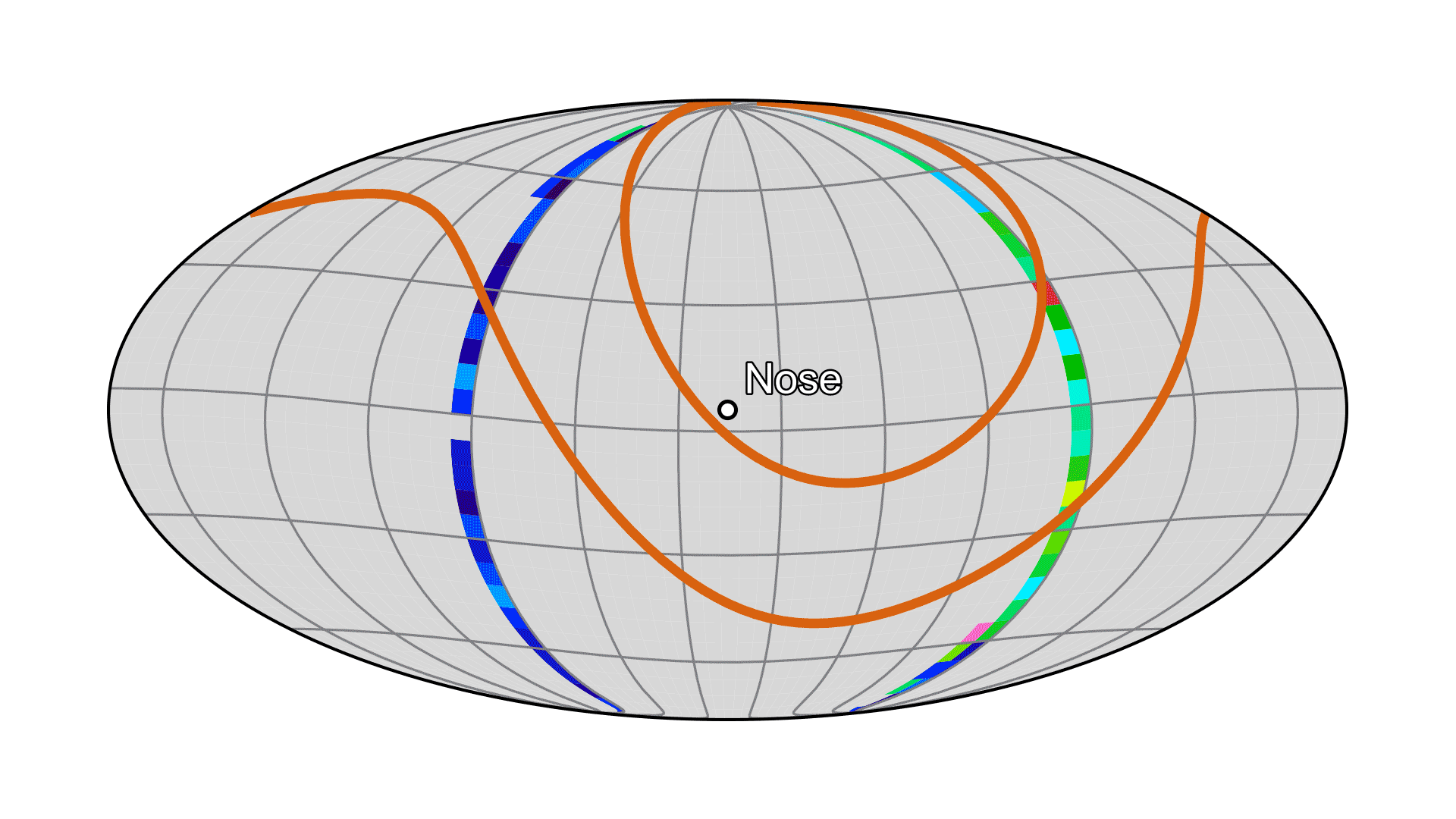
To map the heliosphere’s boundaries, IMAP is equipped with three instruments that measure energetic neutral atoms: IMAP-Lo, IMAP-Hi, and IMAP-Ultra. These uncharged particles, called ENAs for short, are cosmic messengers formed at the heliosphere’s edge that allow scientists to study the boundary region and its variability from afar.
These partial maps of the heliosphere’s boundaries were compiled from first-light data from the IMAP-Hi, IMAP-Lo, and IMAP-Ultra instruments. These initial looks offer a first glimpse at the detail NASA’s IMAP (Interstellar Mapping and Acceleration Probe) will be able to capture. The warmer colors show regions with more energetic neutral atoms (ENAs).NASA“It’s just astounding that within the first couple weeks of observations, we see such clear and consistent ENA data across the factor of 10,000 in energy covered collectively by the three imagers,” said David McComas, Princeton University professor and principal investigator for the IMAP mission. “This, plus excellent first light data from all seven of the other instruments, makes for a 10 out of 10, A-plus start to the mission.”
As IMAP travelled away from Earth, the IMAP-Ultra instrument looked back at the planet and picked up ENAs created by Earth’s magnetic environment. These terrestrially made ENAs, which overwhelm ENAs coming from the heliosphere in sheer numbers, is a reason why IMAP will be stationed at L1. There the spacecraft will have an unobstructed view of ENAs coming from the heliosphere’s boundaries.
Earth’s magnetic environment can be seen glowing bright in this image taken by the IMAP-Ultra instrument, which includes ENA data as well as noise. Earth sits at the center of the red donut-shaped structure. This image was taken as IMAP left Earth for its post at Lagrange point 1.NASAThe mission will also study the solar wind, a continuous flow of charged particles coming from the Sun. Solar wind observations from five of IMAP’s instruments will be used by the IMAP Active Link for Real-Time (I-ALiRT) system to provide roughly a half hour’s warning to voyaging astronauts and spacecraft near Earth about harmful space weather and radiation coming their way. The IMAP instruments are already making near-real-time solar wind measurements that can be used to support space weather forecasts. The I-ALiRT network is being exercised and will be ready for space weather forecasters when IMAP starts its regular science mission at L1.
With all of IMAP’s instruments up and running, the mission has nearly completed its commissioning stage and will arrive at L1 in early January. The mission is now working to complete the final commissioning steps and instrument calibration with the goal of being ready to take operational science data starting Saturday, Feb. 1, 2026.
Here’s a look at IMAP’s instruments and what they’ve seen in their first-light observations.
IMAP-Lo, IMAP-Hi, and IMAP-UltraThe three ENA (energetic neutral atom) instruments, IMAP-Lo, IMAP-Hi, and IMAP-Ultra, will help construct maps of the boundaries of the heliosphere, which will advance our understanding of how the solar wind interacts with our local galaxy. The green streak in this image from IMAP-Hi shows the instrument’s ability to separate ENAs from other particles such as cosmic rays (green and yellow blob).NASA MAGThe magnetometer instrument measures magnetic fields from the Sun that stretch across the solar system. Its first-light data clearly shows dynamic changes in the solar wind’s magnetic field due to a shockwave created by the solar wind (squiggles at right).NASA SWAPIThe Solar Wind and Pickup Ions (SWAPI) instrument measures ions from the solar wind and charged particles from beyond the solar system. Initial data from SWAPI showed a change in the composition of the solar wind over one day. This image shows particles from a coronal mass ejection on Nov. 11 and 12, 2025.NASA CoDICEThe Compact Dual Ion Composition Experiment (CoDICE) instrument measures ions from the solar wind and charged particles from beyond the solar system. It detected different types of oxygen, hydrogen, and helium atoms in its first-light data.NASA HITThe High-energy Ion Telescope (HIT) measures energetic ions and electrons from the Sun. Early ion data shows the common elements up through iron.NASA GLOWSUnlike other IMAP instruments that study particles, the GLObal Solar Wind Structure (GLOWS) instrument images ultraviolet light called the helioglow that is created in part by the solar wind. The first data taken with GLOWS showed helioglow and bright stars, matching scientists’ expectations for the instrument. Unexpectedly, the signature of comet C/2025 K1 (ATLAS), shown by the first small bump from the left in the image, was also seen before it disappeared from GLOWS’ view.NASA SWEAs its name suggests, the Solar Wind Electron (SWE) instrument measures electrons from the solar wind. In its first data collection, SWE successfully captured electrons at a range of energy levels. On Nov. 12, a solar storm passed through the solar system and SWE captured the resulting spike in the number of electrons at each energy level.NASA IDEXThe Interstellar Dust Experiment (IDEX) measures cosmic dust — conglomerations of particles originating outside of the solar system that are smaller than a grain of sand. Prior to IMAP, few of these dust particles had been measured. With two new detections already completed, IDEX has demonstrated its ability to become an unrivaled dust detector. This observation of one of the dust particles shows tentative identifications of the particle’s chemical composition, which includes carbon, oxygen, magnesium, silicon, and hydrogen sulfide.NASA
By Mara Johnson-Groh
NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center, Greenbelt, Md.
Explore More
3 min readNASA’s Carruthers Geocorona Observatory Reveals ‘First Light’ Images
Article 45 minutes ago 5 min readNASA’s Roman Telescope Will Observe Thousands of Newfound Cosmic Voids
Lee esta nota de prensa en español aquí. Our universe is filled with galaxies, in all…
Article 1 day ago 3 min readNASA’s Webb, Curiosity Named in TIME’s Best Inventions Hall of Fame
Article 4 days ago Keep ExploringDiscover Related Topics
Missions
Humans in Space
Climate Change
Solar System